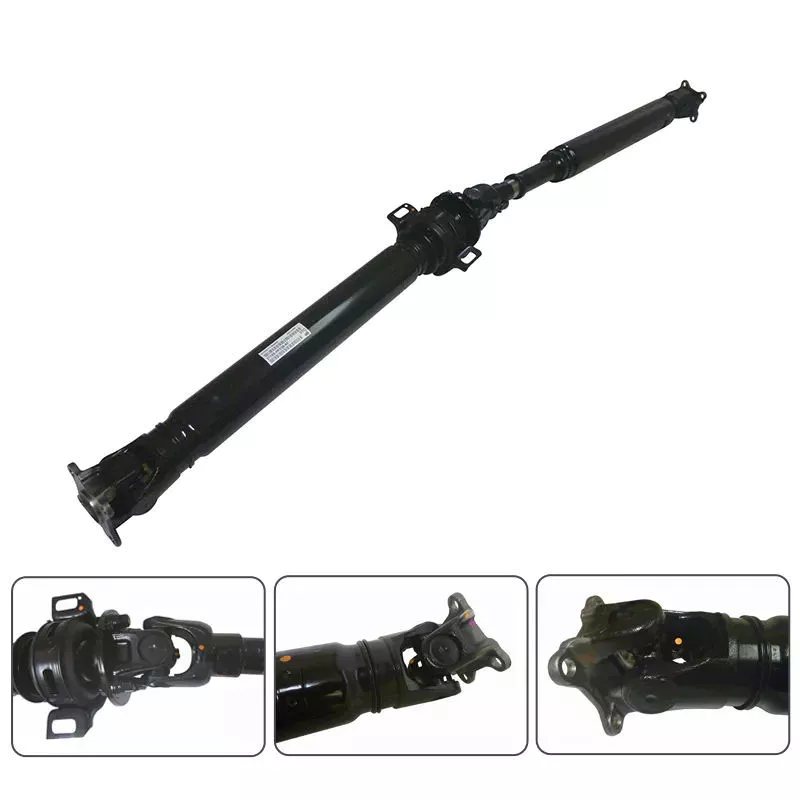
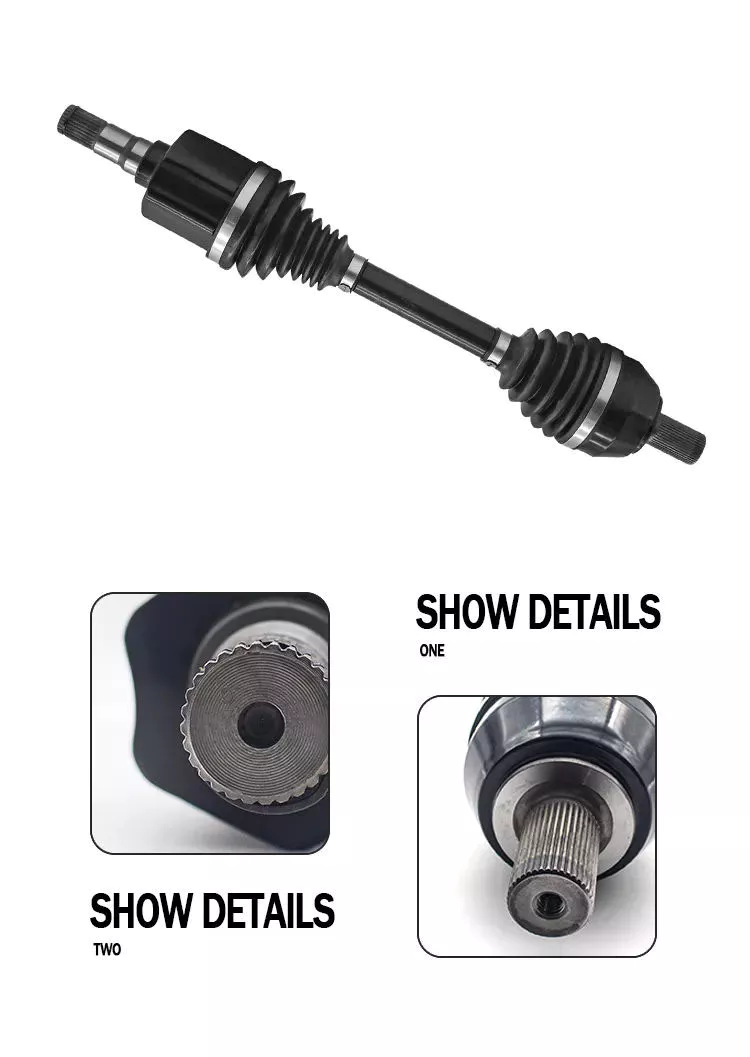
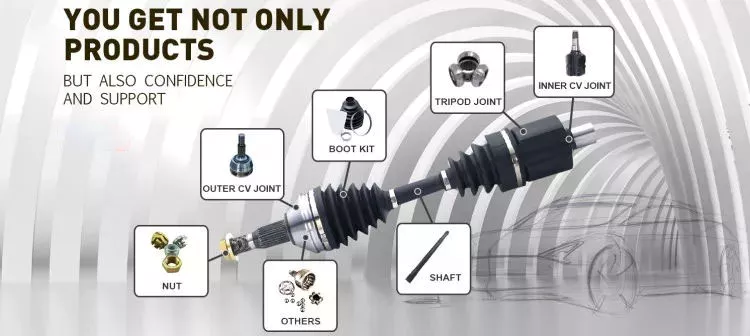
Product Description
Product Description/parameter:
Cummins: 4BT 6BT 6BT-B 6CT 6CT-C NH220 NH250 NT855 NT855-N NH220 NH250 NT855 NT855-N NH14-R K1 9 K6 K19-K19 K6-K6 VTA28 VTA28- K38 KV50 LT10 M11 LT10-10 M11-
Mitsubishi: 4D30 4D34 6D31 6D34 8DC8 8DC8NEW 8DC9 6D14 S4E S6K 4M40 4D55 6D22 4DQ5/4QE 4DR5 S6A S6B S6AMD S12N 6DB1
Komatsu: 4D92 4D94 4D94E 4D95 4D105-1 4D105-3 4D120 6D95 6D95-
L 6D102 6D105 S6D105 6D110 S6D110 SAD110 6D108 6D125 S6S125 SA6D125 6D155 S6D155 SA6D155 6D130 S6D140 6D170
Isuzu: 6BD1 6BB1 6BF1 6BG1 4BD1 4BD1-
T 4BD2 4BG1 DA120 DA640 4BA1 4BB1 4BC2 4BE1 C221 C240 6HE1 6HF1 6HK1 4HF1 4JA1 4JB1 6SD1 6RB1 E120 10PA1 10PD1
Hino: EF100 EF550 EF750 EF350 EF500 EH700 EH500 EH300 EH100 HO6C HO7C HO6B EK100 EK200 EB100 EK200 EB100 EB200 EB300 EB400 EM100 EP100-T EL100 W06D WO6DT HO7D
Nissan: PD6 PE6 RD8 NE6 ND6 PP6H RD8 RF8 RE8 ED30 ED33 FD35 LD23 BD30 ED33 ED6 FD6 FE6 FE6-T SD20 SD25 T23 T25 T27 T27-T
C.A.T.: 3204D379 G379 3406 C13
Deutz: BF6M1013 BF6M1015 BF8L413 KHD413 F3L912D F3L912D F3L913D
Daewoo: 2848.000 D-2366 D-1146
Yanmar: 3TNE84 4D88 4TNE94/4TNV94
Volvo: TD60/61/50 TD70/71 THD101G TD120/121/122/123 TW731 TD100/101 D6D D6E D12D P16
Mercedes-Bens: OM102/104 OM110 OM402 OM355 OM352 OM314
Production accessories
other products
Our Company
Belt Way International Trading Co.,Ltd. was founded in 2008. Specializing in the production and sales of various auto parts. With the spirit of continuous innovation and excellent technical concept, Beltway focuses on the development and improvement of products, and is committed to providing the best quality products to meet the various needs of customers. Technology creates the Future,.look forwarding your inquiry.
Packaging & Delivery
FAQ
1. Q:Are you a Manufacturer or Trading company?
A: We are manufacturer and we have our own factory in ZheJiang province, China.You are welcomed to visit our factory.
2. Q:How long do you need to finish?
A:It usually takes round 20-30 days
3. Q:How about your after-sale service?
A: We provide technical support, etc for your all life once we have reached the deal and placed order from us.
Applications of Spline Couplings
A spline coupling is a highly effective means of connecting 2 or more components. These types of couplings are very efficient, as they combine linear motion with rotation, and their efficiency makes them a desirable choice in numerous applications. Read on to learn more about the main characteristics and applications of spline couplings. You will also be able to determine the predicted operation and wear. You can easily design your own couplings by following the steps outlined below.
Optimal design
The spline coupling plays an important role in transmitting torque. It consists of a hub and a shaft with splines that are in surface contact without relative motion. Because they are connected, their angular velocity is the same. The splines can be designed with any profile that minimizes friction. Because they are in contact with each other, the load is not evenly distributed, concentrating on a small area, which can deform the hub surface.
Optimal spline coupling design takes into account several factors, including weight, material characteristics, and performance requirements. In the aeronautics industry, weight is an important design factor. S.A.E. and ANSI tables do not account for weight when calculating the performance requirements of spline couplings. Another critical factor is space. Spline couplings may need to fit in tight spaces, or they may be subject to other configuration constraints.
Optimal design of spline couplers may be characterized by an odd number of teeth. However, this is not always the case. If the external spline's outer diameter exceeds a certain threshold, the optimal spline coupling model may not be an optimal choice for this application. To optimize a spline coupling for a specific application, the user may need to consider the sizing method that is most appropriate for their application.
Once a design is generated, the next step is to test the resulting spline coupling. The system must check for any design constraints and validate that it can be produced using modern manufacturing techniques. The resulting spline coupling model is then exported to an optimisation tool for further analysis. The method enables a designer to easily manipulate the design of a spline coupling and reduce its weight.
The spline coupling model 20 includes the major structural features of a spline coupling. A product model software program 10 stores default values for each of the spline coupling's specifications. The resulting spline model is then calculated in accordance with the algorithm used in the present invention. The software allows the designer to enter the spline coupling's radii, thickness, and orientation.
Characteristics
An important aspect of aero-engine splines is the load distribution among the teeth. The researchers have performed experimental tests and have analyzed the effect of lubrication conditions on the coupling behavior. Then, they devised a theoretical model using a Ruiz parameter to simulate the actual working conditions of spline couplings. This model explains the wear damage caused by the spline couplings by considering the influence of friction, misalignment, and other conditions that are relevant to the splines' performance.
In order to design a spline coupling, the user first inputs the design criteria for sizing load carrying sections, including the external spline 40 of the spline coupling model 30. Then, the user specifies torque margin performance requirement specifications, such as the yield limit, plastic buckling, and creep buckling. The software program then automatically calculates the size and configuration of the load carrying sections and the shaft. These specifications are then entered into the model software program 10 as specification values.
Various spline coupling configuration specifications are input on the GUI screen 80. The software program 10 then generates a spline coupling model by storing default values for the various specifications. The user then can manipulate the spline coupling model by modifying its various specifications. The final result will be a computer-aided design that enables designers to optimize spline couplings based on their performance and design specifications.
The spline coupling model software program continually evaluates the validity of spline coupling models for a particular application. For example, if a user enters a data value signal corresponding to a parameter signal, the software compares the value of the signal entered to the corresponding value in the knowledge base. If the values are outside the specifications, a warning message is displayed. Once this comparison is completed, the spline coupling model software program outputs a report with the results.
Various spline coupling design factors include weight, material properties, and performance requirements. Weight is 1 of the most important design factors, particularly in the aeronautics field. ANSI and S.A.E. tables do not consider these factors when calculating the load characteristics of spline couplings. Other design requirements may also restrict the configuration of a spline coupling.
Applications
Spline couplings are a type of mechanical joint that connects 2 rotating shafts. Its 2 parts engage teeth that transfer load. Although splines are commonly over-dimensioned, they are still prone to fatigue and static behavior. These properties also make them prone to wear and tear. Therefore, proper design and selection are vital to minimize wear and tear on splines. There are many applications of spline couplings.
A key design is based on the size of the shaft being joined. This allows for the proper spacing of the keys. A novel method of hobbing allows for the formation of tapered bases without interference, and the root of the keys is concentric with the axis. These features enable for high production rates. Various applications of spline couplings can be found in various industries. To learn more, read on.
FE based methodology can predict the wear rate of spline couplings by including the evolution of the coefficient of friction. This method can predict fretting wear from simple round-on-flat geometry, and has been calibrated with experimental data. The predicted wear rate is reasonable compared to the experimental data. Friction evolution in spline couplings depends on the spline geometry. It is also crucial to consider the lubrication condition of the splines.
Using a spline coupling reduces backlash and ensures proper alignment of mated components. The shaft's splined tooth form transfers rotation from the splined shaft to the internal splined member, which may be a gear or other rotary device. A spline coupling's root strength and torque requirements determine the type of spline coupling that should be used.
The spline root is usually flat and has a crown on 1 side. The crowned spline has a symmetrical crown at the centerline of the face-width of the spline. As the spline length decreases toward the ends, the teeth are becoming thinner. The tooth diameter is measured in pitch. This means that the male spline has a flat root and a crowned spline.
Predictability
Spindle couplings are used in rotating machinery to connect 2 shafts. They are composed of 2 parts with teeth that engage each other and transfer load. Spline couplings are commonly over-dimensioned and are prone to static and fatigue behavior. Wear phenomena are also a common problem with splines. To address these issues, it is essential to understand the behavior and predictability of these couplings.
Dynamic behavior of spline-rotor couplings is often unclear, particularly if the system is not integrated with the rotor. For example, when a misalignment is not present, the main response frequency is 1 X-rotating speed. As the misalignment increases, the system starts to vibrate in complex ways. Furthermore, as the shaft orbits depart from the origin, the magnitudes of all the frequencies increase. Thus, research results are useful in determining proper design and troubleshooting of rotor systems.
The model of misaligned spline couplings can be obtained by analyzing the stress-compression relationships between 2 spline pairs. The meshing force model of splines is a function of the system mass, transmitting torque, and dynamic vibration displacement. This model holds when the dynamic vibration displacement is small. Besides, the CZPT stepping integration method is stable and has high efficiency.
The slip distributions are a function of the state of lubrication, coefficient of friction, and loading cycles. The predicted wear depths are well within the range of measured values. These predictions are based on the slip distributions. The methodology predicts increased wear under lightly lubricated conditions, but not under added lubrication. The lubrication condition and coefficient of friction are the key factors determining the wear behavior of splines.